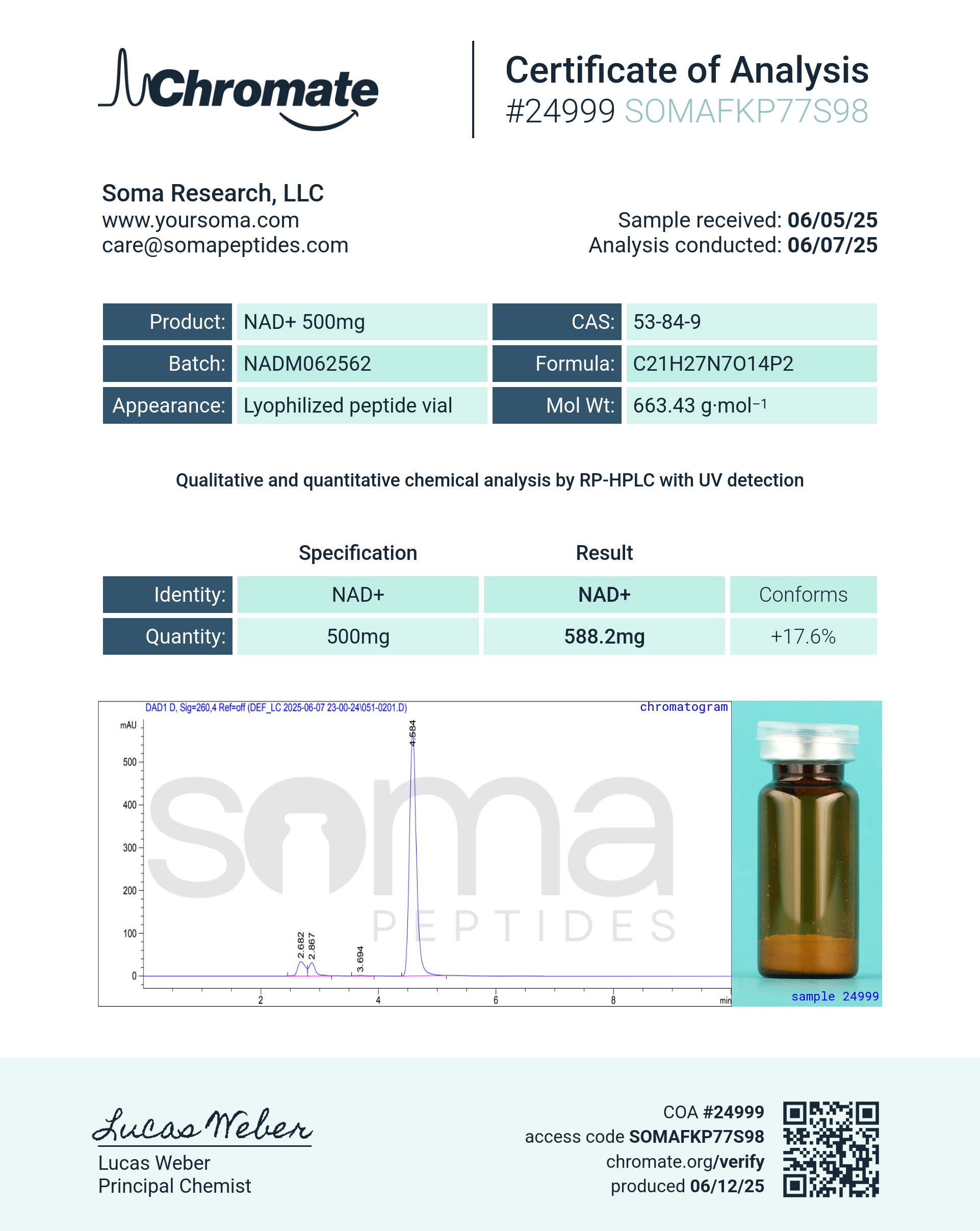
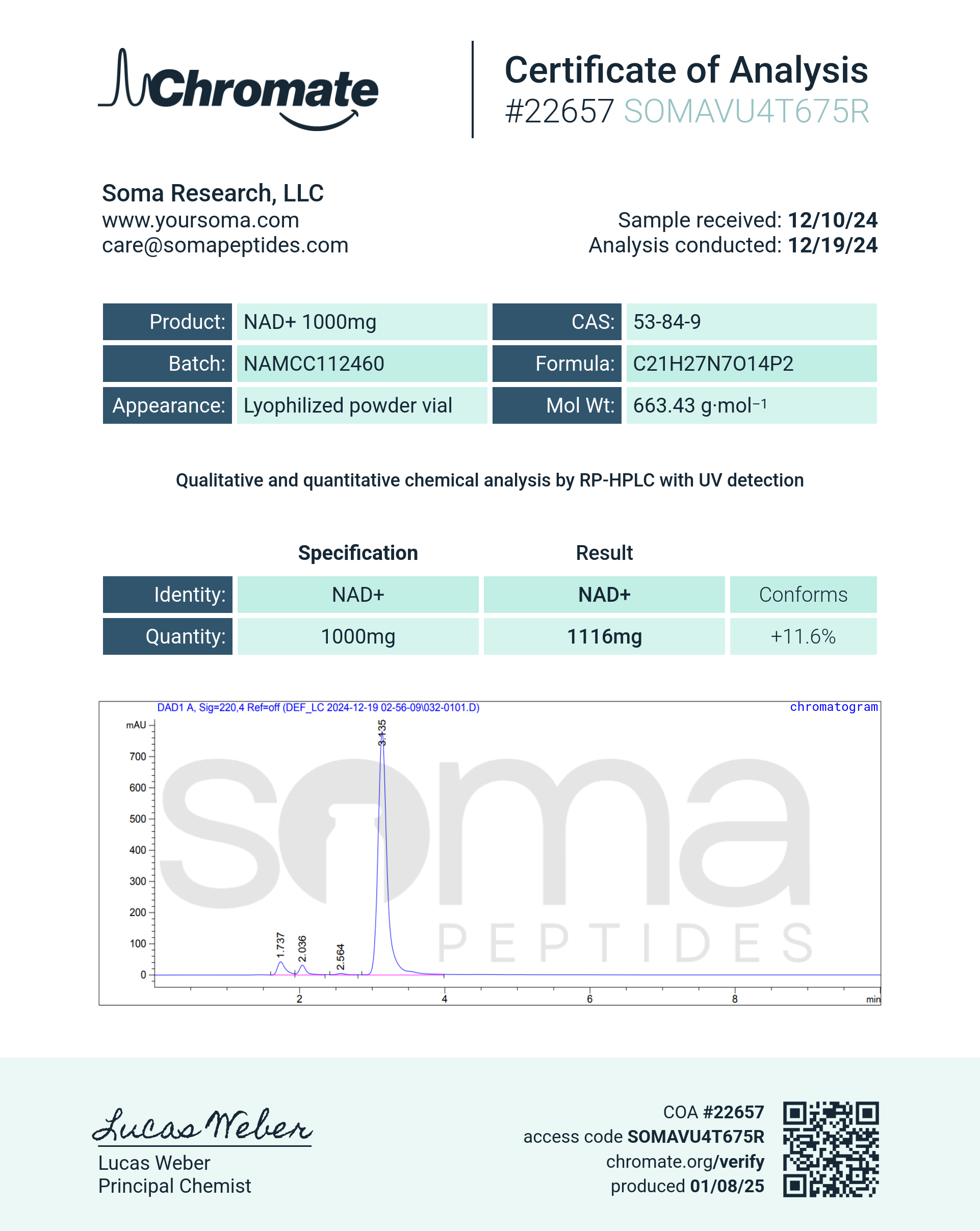
NAD+

Proper Handling
- Reconstitute with Bacteriostatic Water
- Specifications: Lyophilized powder in 10 mL vial. Purity meets or exceeds U.S. Pharmacopeia (USP) regulations.
- Storage: In lyophilized form, the peptide is stable for 2 years. Protect from light. Refrigerate and use within 4-6 weeks after opening or reconstituting.
NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) is a crucial coenzyme found in every living cell that plays a central role in numerous biological processes, including cellular energy production, DNA repair, gene expression, and cellular defense mechanisms. NAD+ acts as a key molecule in redox reactions, facilitating the transfer of electrons and promoting the conversion of nutrients into energy (ATP) through metabolic pathways like glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
As people age, levels of NAD+ in the body naturally decline. This decrease in NAD+ is associated with several age-related health issues, including reduced energy production, impaired DNA repair, increased oxidative stress, and metabolic disorders. Restoration of NAD+ levels has been shown to promote better health in aging individuals by improving energy metabolism, DNA repair, and cellular resilience. Increasing NAD+ levels is also thought to activate sirtuins, which enhance mitochondrial function and extend healthy lifespan.
Science-Backed Research
- Supports cellular energy production
- Enhances mitochondrial function
- Promotes healthy aging
- Boosts DNA repair
- Improves cognitive function
- Supports metabolic health
- Enhances muscle function and recovery
Disclaimer: This peptide is for research and educational purposes only. It is not intended for diagnostic or therapeutic use without the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional.
The products sold on this website are intended for research use only, unless prescribed by a licensed physician or you received authorization under the Right to Try Act Public Law No: 115-176. Always consult with a healthcare provider or medical professional before starting any treatment. Please refer to our terms and conditions prior to purchase.
This product comes in the form of lyophilized powder and must be reconstituted with bacteriostatic water prior to use.
Safety Information: Keep this product out of the reach of children. This product may have limited research available about it and may result in adverse effects if improperly handled. This product is not a dietary supplement, but a pure substance, sold as a raw product. We attest exclusively to the quality, purity and description of the products we provide. This product is for use and handling only by persons with the knowledge and equipment to safely handle this product. You agree to indemnify us for any adverse effects that may arise from improper handling of this product.
The articles and information on products that may be found on this website are provided exclusively for the purposes of providing information and education. The Food and Drug Administration has not reviewed these products or given permission for the treatment or prevention of any disease, medical condition, or ailment using them.
Frequently Asked Questions
NAD+
-
NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) is a coenzyme found in every living cell, essential for energy production, DNA repair, and cellular health. It plays a critical role in supporting mitochondrial function, promoting metabolic efficiency, and combating oxidative stress.
-
NAD+ supplementation has been associated with:
- Improved cellular energy production.
- Enhanced cognitive function and mental clarity.
- Support for DNA repair and healthy aging.
- Better metabolic and mitochondrial health.
-
While NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) and NR (Nicotinamide Riboside) are NAD+ precursors that need to convert into NAD+ in the body, NAD+ is administered in its active form, bypassing the conversion process. This allows for direct support of cellular processes.
-
NAD+ supports cellular repair and mitochondrial function, which are key factors in healthy aging. While it’s not a "cure" for aging, it helps combat the effects of oxidative stress, DNA damage, and energy depletion associated with aging.
-
Highly pure NAD+ is more prone to crystallization because it contains fewer impurities, allowing its molecules to form an orderly crystalline structure. This does not affect the product’s efficacy or safety.
-
No, we do not add buffers to our NAD+. We believe in providing the purest NAD+ available, ensuring the highest quality for our clients.
-
Simply reconstitute as normal using the appropriate sterile solvent. The peptide will dissolve normally and is ready for use. Crystallization is a natural property of high-purity NAD+ and does not compromise its effectiveness.
-
NAD+ is generally well-tolerated, but some individuals may experience mild side effects, including:
- Flushing or warmth during or after administration.
- Mild nausea or upset stomach.
- Temporary headache or fatigue.
-
- Store the lyophilized NAD+ vial in a cool, dry place, away from light.
- After reconstitution, refrigerate the solution and use it within the recommended timeframe as advised.
-
We're happy to help answer questions you may have, or refer you to a licensed healthcare professional. Email us at care@somapeptides.com or schedule a consult.
Cellular medicine is only the beginning.
Embarking on the journey to understand cellular medicine through peptides involves embracing holistic well-being through consultative care. Schedule an appointment with a peptide specialist to get support and protocols.