GHK-Cu Copper

Proper Handling
- Reconstitute with Bacteriostatic Water
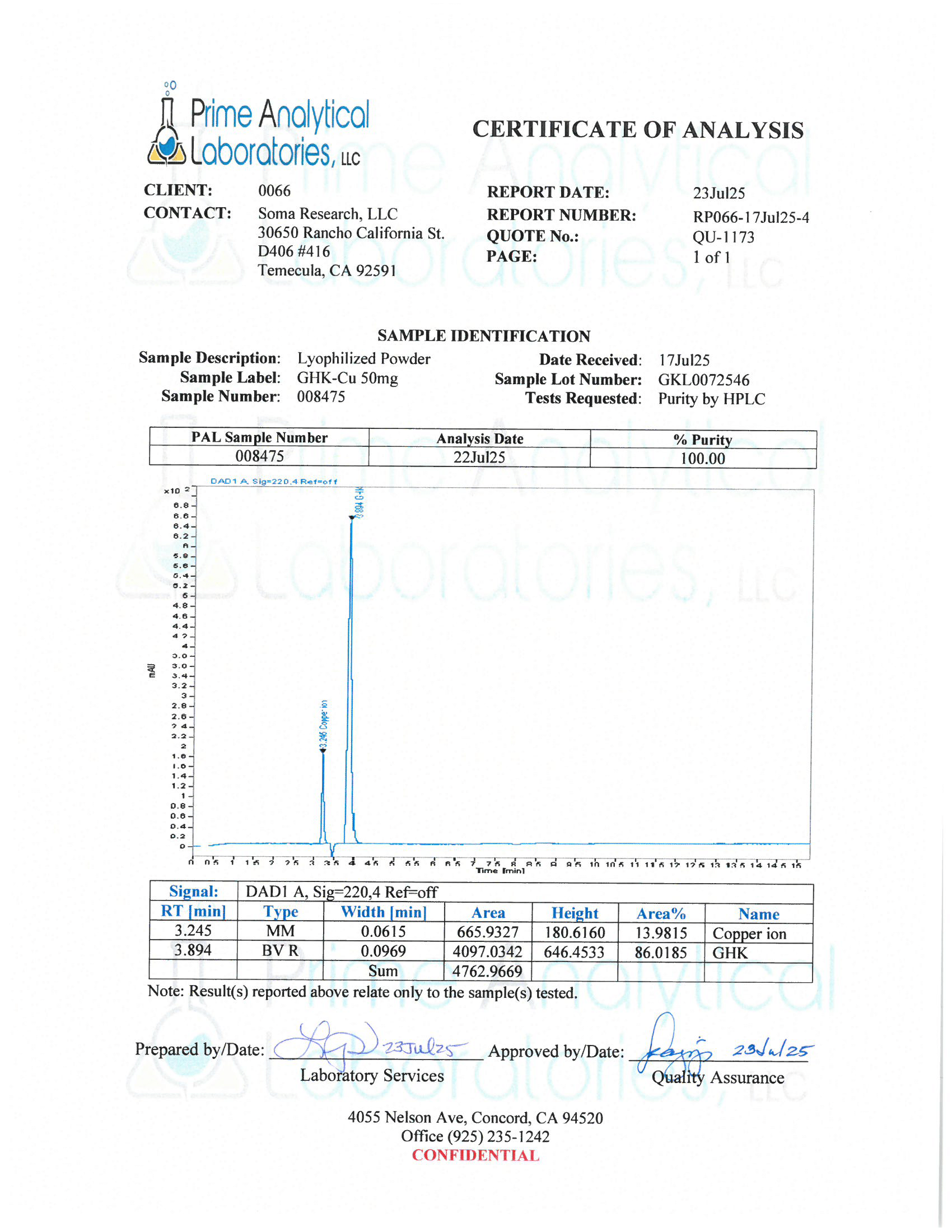
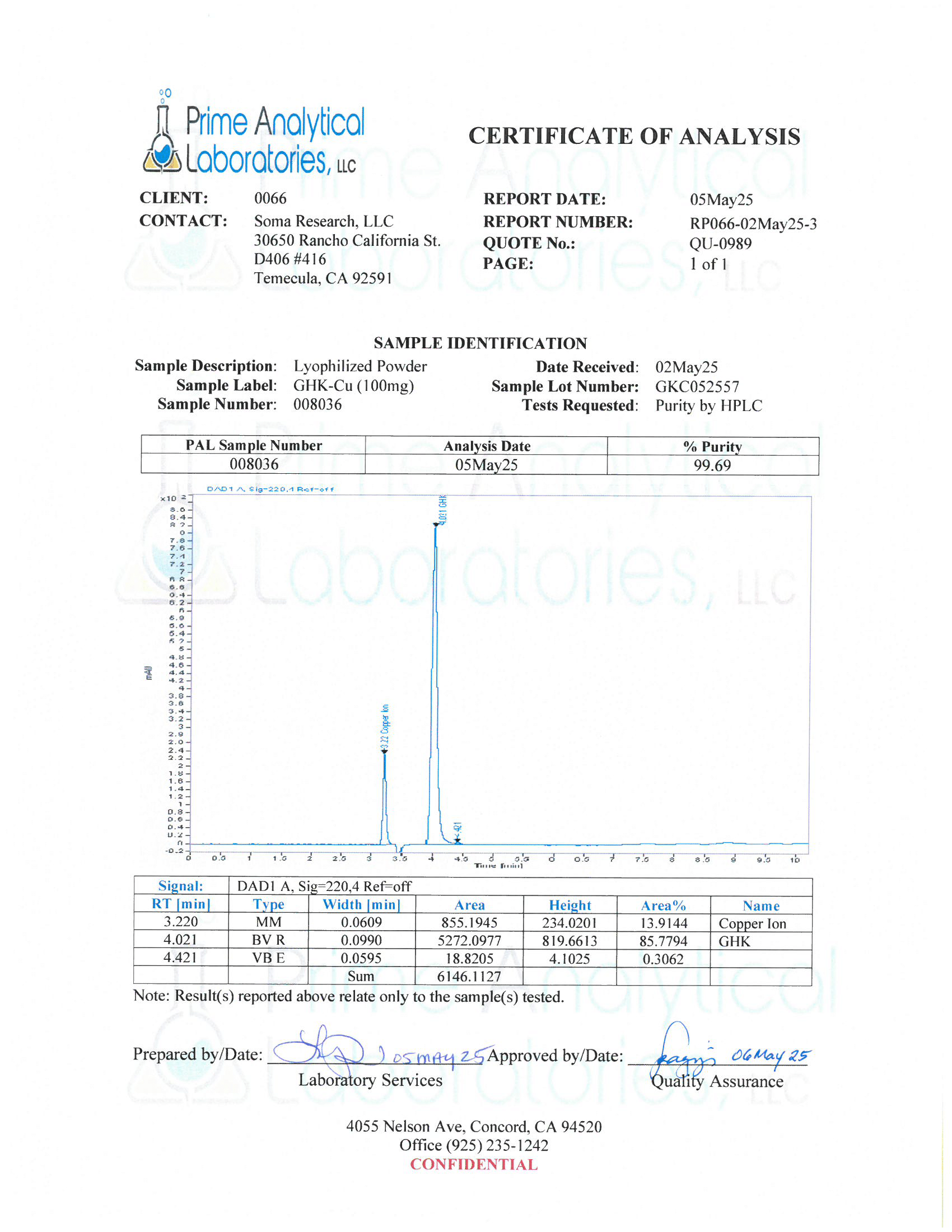
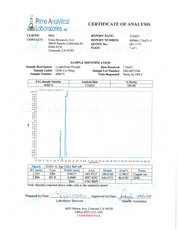
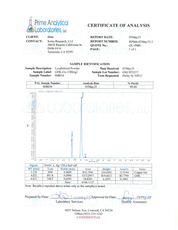
- Specifications: Lyophilized powder. Purity (>98%) meets or exceeds U.S. Pharmacopeia (USP) regulations.
- Storage: In lyophilized form, the peptide is stable for 2 years. Protect from light. Refrigerate and use within 45 days after opening or reconstituting.
GHK-Cu (Glycyl-L-Histidyl-L-Lysine-Copper) is a naturally occurring copper peptide found in the human body. It is composed of three amino acids bound to a copper ion and is known for its regenerative properties. GHK-Cu plays a significant role in wound healing, tissue repair, reducing inflammation, and reversing signs of aging. Growing in popularity is the
Science-Backed Research
- Promotes Collagen Production
- Accelerates Wound Healing
- Reduces Inflammation
- Stimulates Hair Growth
- Enhances Skin Regeneration
- Provides Antioxidant Protection
- Improves Skin Barrier Function
- Supports Copper Transport
Disclaimer: This peptide is for research and educational purposes only. It is not intended for diagnostic or therapeutic use without the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional.
The products sold on this website are intended for research use only, unless prescribed by a licensed physician or you received authorization under the Right to Try Act Public Law No: 115-176. Always consult with a healthcare provider or medical professional before starting any treatment. Please refer to our terms and conditions prior to purchase.
This product comes in the form of lyophilized powder and must be reconstituted with bacteriostatic water prior to use.
Safety Information: Keep this product out of the reach of children. This product may have limited research available about it and may result in adverse effects if improperly handled. This product is not a dietary supplement, but a pure substance, sold as a raw product. We attest exclusively to the quality, purity and description of the products we provide. This product is for use and handling only by persons with the knowledge and equipment to safely handle this product. You agree to indemnify us for any adverse effects that may arise from improper handling of this product.
The articles and information on products that may be found on this website are provided exclusively for the purposes of providing information and education. The Food and Drug Administration has not reviewed these products or given permission for the treatment or prevention of any disease, medical condition, or ailment using them.
Frequently Asked Questions
GHK-Cu Copper
-
GHK-Cu (Glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine-Copper) is a copper peptide complex naturally occurring in the human body. It plays a crucial role in wound healing, skin repair, inflammation control, and overall tissue regeneration. GHK-Cu has been studied extensively for its regenerative and anti-aging properties, particularly in skin and hair care, but its benefits extend to various areas of health.
-
GHK-Cu (glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine copper) is blue because of the copper (Cu) ion bound to the GHK peptide. The blue color arises due to the way copper interacts with light when it forms a complex with certain molecules, in this case, the GHK peptide.
This blue hue is characteristic of copper peptides and does not affect their biological function. The blue color is a visual indicator of the presence of copper in the GHK-Cu molecule.
- Copper can exist in different oxidation states, but GHK-Cu contains copper in the +2 oxidation state (Cu²⁺).
- When copper (Cu²⁺) is bound to the GHK peptide, it forms a complex that absorbs light in a specific range of the visible spectrum. This causes the compound to appear blue, a common property of copper complexes.
- The blue color is particularly associated with the d-d electron transitions of copper ions when they are coordinated with certain ligands, like histidine (an amino acid in the GHK peptide). These transitions absorb light in the red and yellow regions of the spectrum, making the complex appear blue.
-
Wound Healing and Skin Repair: GHK-Cu promotes collagen production and assists in tissue remodeling, making it effective for healing wounds, reducing scars, and improving skin elasticity and firmness.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties: It can reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, which contributes to healthier skin and overall healing.
Anti-Aging Effects: By stimulating collagen production and increasing skin’s structural proteins, GHK-Cu helps reduce the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and hyperpigmentation.
Hair Growth: GHK-Cu has been shown to stimulate hair growth by increasing hair follicle size and reducing hair thinning.
Antioxidant Properties: The peptide acts as a powerful antioxidant, protecting cells from oxidative damage.
Tissue Regeneration: It assists in the regeneration of various tissues, including lungs and liver, due to its ability to modulate gene expression related to tissue repair.
-
GHK-Cu Copper can be injected subcutaneously (under the skin) for systemic benefits, such as improving tissue repair, reducing inflammation, or promoting overall skin health. This method is commonly used in medical settings.
GHK-Cu Copper is for research purposes only, unless prescribed by a licensed physician.
-
Blending GHK-Cu with BPC-157 can make the injection less painful. BPC-157 has anti-inflammatory and healing properties, which can help reduce irritation or discomfort that sometimes occurs with peptide injections. This combination helps improve tissue repair while minimizing any potential injection site pain or sensitivity.
While GHK-Cu is generally well-tolerated, some potential side effects include:
- Injection site reactions: Redness, itching, or mild discomfort at the injection site.
- Allergic reactions: Though rare, some may experience allergic responses such as swelling, rash, or hives.
- Temporary skin discoloration: In some cases, it may cause mild, temporary blue or green skin tint due to the copper content.
- Systemic effects: Rarely, it may lead to headaches, dizziness, or nausea.
-
We're happy to help answer questions you may have, or refer you to a licensed healthcare professional. Email us at care@somapeptides.com or schedule a consult.