MOTS-c

Proper Handling
- Reconstitute with Bacteriostatic Water
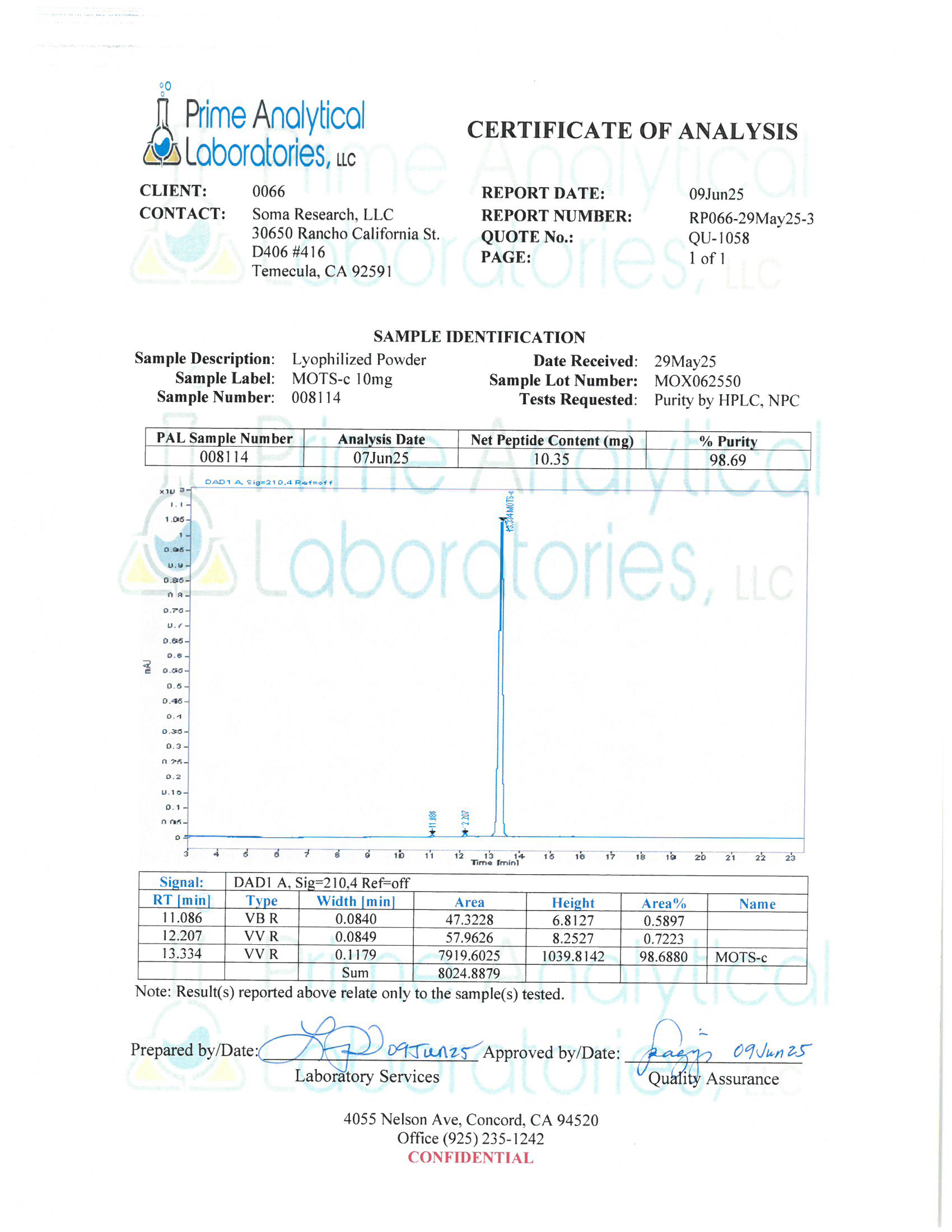
- Specifications: Lyophilized powder. Purity (>98%) meets or exceeds U.S. Pharmacopeia (USP) regulations.
- Storage: In lyophilized form, the peptide is stable for 2 years. Protect from light. Refrigerate and use within 45 days after opening or reconstituting.
MOTS-c is a 16 amino acid peptide that is coded by the mitochondrial genome. The mitochondria are the “power generators” in cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use. According to research, mitochondrial-derived peptides such as MOTS-c have a role in maintaining mitochondrial function and protecting cells under different stresses. It has been shown that exercise causes MOTS-c levels to go up.
MOTS-c peptide may help reduce insulin resistance, prevent obesity, improve muscle function, promote bone metabolism, enhance immune regulation, and postpone aging.
Science-Backed Research
- Promotes fatty acid metabolism in the liver
- Promotes metabolic flexibility and homeostasis
- Helps regulate mitochondrial energy
- Protects against age and diet dependent insulin resistance and obesity
- Promotes resistance to metabolic stress
- Improves exercise capacity
- Helps prevent osteoporosis
- Improves glucose regulation
- Promotes cell differentiation to form osteoblasts
Disclaimer: This peptide is for research and educational purposes only. It is not intended for diagnostic or therapeutic use without the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional.
This product is for research and educational purposes only. It is not intended for diagnostic or therapeutic use without the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional. Please refer to our terms and conditions prior to purchase.
This product comes in the form of lyophilized powder and must be reconstituted with bacteriostatic water prior to use.
Safety Information: Keep this product out of the reach of children. This material has limited research available about it and may result in adverse effects if improperly handled or consumed. This product is not a dietary supplement, but a pure substance, sold as a raw material. We attest exclusively to the quality, purity and description of the materials we provide. This product is for use and handling only by persons with the knowledge and equipment to safely handle this material. You agree to indemnify us for any adverse effects that may arise from improper handling and/or consumption of this product.
The articles and information on products that may be found on this website are provided exclusively for the purposes of providing information and education. These items are not pharmaceuticals or medications, and the Food and Drug Administration has not given permission for the treatment or prevention of any disease, medical condition, or ailment using them.
Frequently Asked Questions
MOTS-c
-
MOTS-c is an injectable peptide. Peptides are typically administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly. Some peptides are available as nasal sprays or oral capsules.
MOTS-c is for research and educational purposes only. It is not intended for diagnostic or therapeutic use without the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional.
-
Most peptides are not bioavailable orally due to degradation in the digestive system. However, some, like BPC-157 or KPV, are effective in capsule form.
-
Synthetic peptides are very similar to peptides that naturally exist in the body and in healthy foods. The FDA has categorized peptides as GRAS (considered to be generally recognized as safe) ingredients.
The side effects of peptides depend on the specific type of peptide and the method of consumption. Some common side effects associated with peptides include:
- Injection site reactions such as redness, pain, swelling, bruising and itching
- Flushing sensation
- Digestive issues like nausea, diarrhea, and other digestive symptoms
- Hormonal imbalances caused by growth hormone-releasing peptides (GHRP)
-
Peptides should be stored in a refrigerator (2°C to 8°C) after reconstitution. Lyophilized (powdered) peptides should also be kept in a cool, dry place until reconstitution or in a freezer for long term storage.
-
Commonly known and understood peptides in the medical community are insulin, oxytocin, collagen. These are all peptides.
As a matter of fact, the human body naturally produces more than 7,000 known peptide types. With this many peptides, they are used in a wide variety of the body's systems and are essential to the way we function and age.
Peptides are very tiny proteins made up of short chains of amino acids. They signal the cells in your body to act in certain ways. As a result, peptides are responsible for how you function, feel, look and live overall. Since different peptides affect different cells and functions, they can be highly tailored and targeted to treat a full spectrum of health, wellness, fitness, metabolism, aging and cognitive conditions.
-
Common uses include:
- Anti-aging and skin rejuvenation
- Weight loss and fat burning
- Muscle growth and recovery
- Enhancing cognitive function
- Improving libido and sexual health
- Treating inflammation and injuries
- Prevention and treatment of diseases
- Addiction treatment and recovery
-
We're happy to help answer questions you may have, or refer you to a licensed professional for advice. Email us at care@somapeptides.com or schedule a consultation.